class cv::Subdiv2D
Overview
#include <imgproc.hpp> class Subdiv2D { public: // enums enum { PTLOC_ERROR = -2, PTLOC_OUTSIDE_RECT = -1, PTLOC_INSIDE = 0, PTLOC_VERTEX = 1, PTLOC_ON_EDGE = 2, }; enum { NEXT_AROUND_ORG = 0x00, NEXT_AROUND_DST = 0x22, PREV_AROUND_ORG = 0x11, PREV_AROUND_DST = 0x33, NEXT_AROUND_LEFT = 0x13, NEXT_AROUND_RIGHT = 0x31, PREV_AROUND_LEFT = 0x20, PREV_AROUND_RIGHT = 0x02, }; // structs struct QuadEdge; struct Vertex; // construction Subdiv2D(); Subdiv2D(Rect rect); // methods int edgeDst( int edge, Point2f* dstpt = 0 ) const; int edgeOrg( int edge, Point2f* orgpt = 0 ) const; int findNearest( Point2f pt, Point2f* nearestPt = 0 ); int getEdge( int edge, int nextEdgeType ) const; void getEdgeList(std::vector<Vec4f>& edgeList) const; void getLeadingEdgeList(std::vector<int>& leadingEdgeList) const; void getTriangleList(std::vector<Vec6f>& triangleList) const; Point2f getVertex( int vertex, int* firstEdge = 0 ) const; void getVoronoiFacetList( const std::vector<int>& idx, std::vector<std::vector<Point2f>>& facetList, std::vector<Point2f>& facetCenters ); void initDelaunay(Rect rect); int insert(Point2f pt); void insert(const std::vector<Point2f>& ptvec); int locate( Point2f pt, int& edge, int& vertex ); int nextEdge(int edge) const; int rotateEdge( int edge, int rotate ) const; int symEdge(int edge) const; protected: // fields Point2f bottomRight; int freePoint; int freeQEdge; std::vector<QuadEdge> qedges; int recentEdge; Point2f topLeft; bool validGeometry; std::vector<Vertex> vtx; // methods void calcVoronoi(); void checkSubdiv() const; void clearVoronoi(); int connectEdges( int edgeA, int edgeB ); void deleteEdge(int edge); void deletePoint(int vtx); int isRightOf( Point2f pt, int edge ) const; int newEdge(); int newPoint( Point2f pt, bool isvirtual, int firstEdge = 0 ); void setEdgePoints( int edge, int orgPt, int dstPt ); void splice( int edgeA, int edgeB ); void swapEdges(int edge); };
Detailed Documentation
Enum Values
PTLOC_ERROR
Point location error.
PTLOC_OUTSIDE_RECT
Point outside the subdivision bounding rect.
PTLOC_INSIDE
Point inside some facet.
PTLOC_VERTEX
Point coincides with one of the subdivision vertices.
PTLOC_ON_EDGE
Point on some edge.
Fields
Point2f bottomRight
Bottom right corner of the bounding rect.
std::vector<QuadEdge> qedges
All of the edges.
Point2f topLeft
Top left corner of the bounding rect.
std::vector<Vertex> vtx
All of the vertices.
Construction
Subdiv2D()
creates an empty Subdiv2D object. To create a new empty Delaunay subdivision you need to use the initDelaunay() function.
Subdiv2D(Rect rect)
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
The function creates an empty Delaunay subdivision where 2D points can be added using the function insert(). All of the points to be added must be within the specified rectangle, otherwise a runtime error is raised.
Parameters:
| rect | – Rectangle that includes all of the 2D points that are to be added to the subdivision. |
Methods
int edgeDst( int edge, Point2f* dstpt = 0 ) const
Returns the edge destination.
Parameters:
| edge | – Subdivision edge ID. |
| dstpt | – Output vertex location. |
Returns:
vertex ID.
int edgeOrg( int edge, Point2f* orgpt = 0 ) const
Returns the edge origin.
Parameters:
| edge | – Subdivision edge ID. |
| orgpt | – Output vertex location. |
Returns:
vertex ID.
int findNearest( Point2f pt, Point2f* nearestPt = 0 )
Finds the subdivision vertex closest to the given point.
The function is another function that locates the input point within the subdivision. It finds the subdivision vertex that is the closest to the input point. It is not necessarily one of vertices of the facet containing the input point, though the facet (located using locate()) is used as a starting point.
Parameters:
| pt | – Input point. |
| nearestPt | – Output subdivision vertex point. |
Returns:
vertex ID.
int getEdge( int edge, int nextEdgeType ) const
Returns one of the edges related to the given edge.
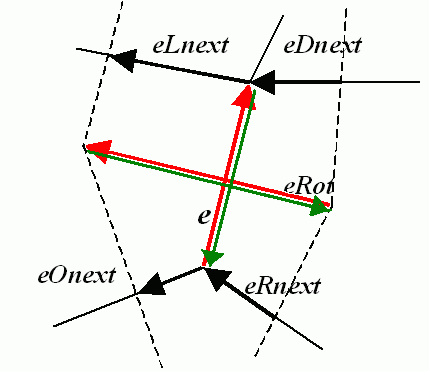
Parameters:
| edge | – Subdivision edge ID. |
| nextEdgeType |
|
Returns:
edge ID related to the input edge.
void getEdgeList(std::vector<Vec4f>& edgeList) const
Returns a list of all edges.
The function gives each edge as a 4 numbers vector, where each two are one of the edge vertices. i.e. org_x = v[0], org_y = v[1], dst_x = v[2], dst_y = v[3].
Parameters:
| edgeList | – Output vector. |
void getLeadingEdgeList(std::vector<int>& leadingEdgeList) const
Returns a list of the leading edge ID connected to each triangle.
The function gives one edge ID for each triangle.
Parameters:
| leadingEdgeList | – Output vector. |
void getTriangleList(std::vector<Vec6f>& triangleList) const
Returns a list of all triangles.
The function gives each triangle as a 6 numbers vector, where each two are one of the triangle vertices. i.e. p1_x = v[0], p1_y = v[1], p2_x = v[2], p2_y = v[3], p3_x = v[4], p3_y = v[5].
Parameters:
| triangleList | – Output vector. |
Point2f getVertex( int vertex, int* firstEdge = 0 ) const
Returns vertex location from vertex ID.
Parameters:
| vertex | – vertex ID. |
| firstEdge | – Optional. The first edge ID which is connected to the vertex. |
Returns:
vertex (x,y)
void getVoronoiFacetList( const std::vector<int>& idx, std::vector<std::vector<Point2f>>& facetList, std::vector<Point2f>& facetCenters )
Returns a list of all Voroni facets.
Parameters:
| idx | – Vector of vertices IDs to consider. For all vertices you can pass empty vector. |
| facetList | – Output vector of the Voroni facets. |
| facetCenters | – Output vector of the Voroni facets center points. |
void initDelaunay(Rect rect)
Creates a new empty Delaunay subdivision.
Parameters:
| rect | – Rectangle that includes all of the 2D points that are to be added to the subdivision. |
int insert(Point2f pt)
Insert a single point into a Delaunay triangulation.
The function inserts a single point into a subdivision and modifies the subdivision topology appropriately. If a point with the same coordinates exists already, no new point is added. If the point is outside of the triangulation specified rect a runtime error is raised.
Parameters:
| pt | – Point to insert. |
Returns:
the ID of the point.
void insert(const std::vector<Point2f>& ptvec)
Insert multiple points into a Delaunay triangulation.
The function inserts a vector of points into a subdivision and modifies the subdivision topology appropriately.
Parameters:
| ptvec | – Points to insert. |
int locate( Point2f pt, int& edge, int& vertex )
Returns the location of a point within a Delaunay triangulation.
The function locates the input point within the subdivision and gives one of the triangle edges or vertices.
Parameters:
| pt | – Point to locate. |
| edge | – Output edge that the point belongs to or is located to the right of it. |
| vertex | – Optional output vertex the input point coincides with. |
Returns:
an integer which specify one of the following five cases for point location:
- The point falls into some facet. The function returns PTLOC_INSIDE and edge will contain one of edges of the facet.
- The point falls onto the edge. The function returns PTLOC_ON_EDGE and edge will contain this edge.
- The point coincides with one of the subdivision vertices. The function returns PTLOC_VERTEX and vertex will contain a pointer to the vertex.
- The point is outside the subdivision reference rectangle. The function returns PTLOC_OUTSIDE_RECT and no pointers are filled.
- One of input arguments is invalid. A runtime error is raised or, if silent or “parent” error processing mode is selected, CV_PTLOC_ERROR is returned.
int nextEdge(int edge) const
Returns next edge around the edge origin.
Parameters:
| edge | – Subdivision edge ID. |
Returns:
an integer which is next edge ID around the edge origin: eOnext on the picture above if e is the input edge).
int rotateEdge( int edge, int rotate ) const
Returns another edge of the same quad-edge.
Parameters:
| edge | – Subdivision edge ID. |
| rotate |
|
Returns:
one of the edges ID of the same quad-edge as the input edge.