Template Matching
Prev Tutorial: Back Projection
Next Tutorial: Finding contours in your image
Goal
In this tutorial you will learn how to:
- Use the OpenCV function matchTemplate() to search for matches between an image patch and an input image
- Use the OpenCV function minMaxLoc() to find the maximum and minimum values (as well as their positions) in a given array.
Theory
What is template matching?
Template matching is a technique for finding areas of an image that match (are similar) to a template image (patch).
While the patch must be a rectangle it may be that not all of the rectangle is relevant. In such a case, a mask can be used to isolate the portion of the patch that should be used to find the match.
How does it work?
We need two primary components:
- Source image (I): The image in which we expect to find a match to the template image
- Template image (T): The patch image which will be compared to the template image
our goal is to detect the highest matching area:
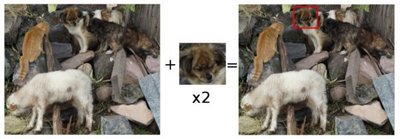
To identify the matching area, we have to compare the template image against the source image by sliding it:

By sliding, we mean moving the patch one pixel at a time (left to right, up to down). At each location, a metric is calculated so it represents how “good” or “bad” the match at that location is (or how similar the patch is to that particular area of the source image).
For each location of T over I, you store the metric in the result matrix R. Each location \((x,y)\) in R contains the match metric:
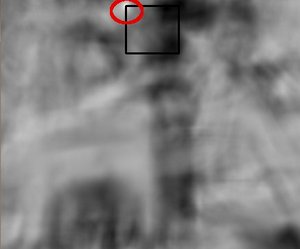
the image above is the result R of sliding the patch with a metric TM_CCORR_NORMED. The brightest locations indicate the highest matches. As you can see, the location marked by the red circle is probably the one with the highest value, so that location (the rectangle formed by that point as a corner and width and height equal to the patch image) is considered the match.
In practice, we locate the highest value (or lower, depending of the type of matching method) in the R matrix, using the function minMaxLoc()
How does the mask work?
If masking is needed for the match, three components are required:
- Source image (I): The image in which we expect to find a match to the template image
- Template image (T): The patch image which will be compared to the template image
- Mask image (M): The mask, a grayscale image that masks the template
Only two matching methods currently accept a mask: CV_TM_SQDIFF and CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED (see below for explanation of all the matching methods available in opencv).
The mask must have the same dimensions as the template
The mask should have a CV_8U or CV_32F depth and the same number of channels as the template image. In CV_8U case, the mask values are treated as binary, i.e. zero and non-zero. In CV_32F case, the values should fall into [0..1] range and the template pixels will be multiplied by the corresponding mask pixel values. Since the input images in the sample have the CV_8UC3 type, the mask is also read as color image.
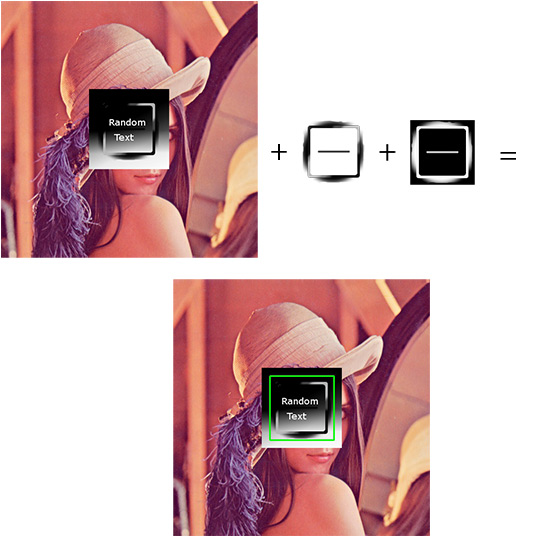
Which are the matching methods available in OpenCV?
Good question. OpenCV implements Template matching in the function matchTemplate(). The available methods are 6:
method=CV_TM_SQDIFF
\[R(x,y)= \sum _{x',y'} (T(x',y')-I(x+x',y+y'))^2\]method=CV_TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
\[R(x,y)= \frac{\sum_{x',y'} (T(x',y')-I(x+x',y+y'))^2}{\sqrt{\sum_{x',y'}T(x',y')^2 \cdot \sum_{x',y'} I(x+x',y+y')^2}}\]method=CV_TM_CCORR
\[R(x,y)= \sum _{x',y'} (T(x',y') \cdot I(x+x',y+y'))\]method=CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED
\[R(x,y)= \frac{\sum_{x',y'} (T(x',y') \cdot I(x+x',y+y'))}{\sqrt{\sum_{x',y'}T(x',y')^2 \cdot \sum_{x',y'} I(x+x',y+y')^2}}\]method=CV_TM_CCOEFF
\[R(x,y)= \sum _{x',y'} (T'(x',y') \cdot I'(x+x',y+y'))\]where
\[\begin{split}\begin{array}{l} T'(x',y')=T(x',y') - 1/(w \cdot h) \cdot \sum _{x'',y''} T(x'',y'') \\ I'(x+x',y+y')=I(x+x',y+y') - 1/(w \cdot h) \cdot \sum _{x'',y''} I(x+x'',y+y'') \end{array}\end{split}\]method=CV_TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
\[R(x,y)= \frac{ \sum_{x',y'} (T'(x',y') \cdot I'(x+x',y+y')) }{ \sqrt{\sum_{x',y'}T'(x',y')^2 \cdot \sum_{x',y'} I'(x+x',y+y')^2} }\]
Code
What does this program do?
- Loads an input image, an image patch (template), and optionally a mask
- Perform a template matching procedure by using the OpenCV function matchTemplate() with any of the 6 matching methods described before. The user can choose the method by entering its selection in the Trackbar. If a mask is supplied, it will only be used for the methods that support masking
- Normalize the output of the matching procedure
- Localize the location with higher matching probability
- Draw a rectangle around the area corresponding to the highest match
Downloadable code : Click here
Code at glance:
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" #include <iostream> using namespace std; using namespace cv; bool use_mask; Mat img; Mat templ; Mat mask; Mat result; const char* image_window = "Source Image"; const char* result_window = "Result window"; int match_method; int max_Trackbar = 5; void MatchingMethod( int, void* ); int main( int argc, char** argv ) { if (argc < 3) { cout << "Not enough parameters" << endl; cout << "Usage:\n./MatchTemplate_Demo <image_name> <template_name> [<mask_name>]" << endl; return -1; } img = imread( argv[1], IMREAD_COLOR ); templ = imread( argv[2], IMREAD_COLOR ); if(argc > 3) { use_mask = true; mask = imread( argv[3], IMREAD_COLOR ); } if(img.empty() || templ.empty() || (use_mask && mask.empty())) { cout << "Can't read one of the images" << endl; return -1; } namedWindow( image_window, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); namedWindow( result_window, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); const char* trackbar_label = "Method: \n 0: SQDIFF \n 1: SQDIFF NORMED \n 2: TM CCORR \n 3: TM CCORR NORMED \n 4: TM COEFF \n 5: TM COEFF NORMED"; createTrackbar( trackbar_label, image_window, &match_method, max_Trackbar, MatchingMethod ); MatchingMethod( 0, 0 ); waitKey(0); return 0; } void MatchingMethod( int, void* ) { Mat img_display; img.copyTo( img_display ); int result_cols = img.cols - templ.cols + 1; int result_rows = img.rows - templ.rows + 1; result.create( result_rows, result_cols, CV_32FC1 ); bool method_accepts_mask = (CV_TM_SQDIFF == match_method || match_method == CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED); if (use_mask && method_accepts_mask) { matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method, mask); } else { matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method); } normalize( result, result, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat() ); double minVal; double maxVal; Point minLoc; Point maxLoc; Point matchLoc; minMaxLoc( result, &minVal, &maxVal, &minLoc, &maxLoc, Mat() ); if( match_method == TM_SQDIFF || match_method == TM_SQDIFF_NORMED ) { matchLoc = minLoc; } else { matchLoc = maxLoc; } rectangle( img_display, matchLoc, Point( matchLoc.x + templ.cols , matchLoc.y + templ.rows ), Scalar::all(0), 2, 8, 0 ); rectangle( result, matchLoc, Point( matchLoc.x + templ.cols , matchLoc.y + templ.rows ), Scalar::all(0), 2, 8, 0 ); imshow( image_window, img_display ); imshow( result_window, result ); return; }
Downloadable code : Click here
Code at glance:
import org.opencv.core.*; import org.opencv.core.Point; import org.opencv.imgcodecs.Imgcodecs; import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent; import javax.swing.event.ChangeListener; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import java.awt.image.DataBufferByte; import java.util.*; class MatchTemplateDemoRun implements ChangeListener{ Boolean use_mask = false; Mat img = new Mat(), templ = new Mat(); Mat mask = new Mat(); int match_method; JLabel imgDisplay = new JLabel(), resultDisplay = new JLabel(); public void run(String[] args) { if (args.length < 2) { System.out.println("Not enough parameters"); System.out.println("Program arguments:\n<image_name> <template_name> [<mask_name>]"); System.exit(-1); } img = Imgcodecs.imread( args[0], Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR ); templ = Imgcodecs.imread( args[1], Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR ); if(args.length > 2) { use_mask = true; mask = Imgcodecs.imread( args[2], Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR ); } if(img.empty() || templ.empty() || (use_mask && mask.empty())) { System.out.println("Can't read one of the images"); System.exit(-1); } matchingMethod(); createJFrame(); } private void matchingMethod() { Mat result = new Mat(); Mat img_display = new Mat(); img.copyTo( img_display ); int result_cols = img.cols() - templ.cols() + 1; int result_rows = img.rows() - templ.rows() + 1; result.create( result_rows, result_cols, CvType.CV_32FC1 ); Boolean method_accepts_mask = (Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF == match_method || match_method == Imgproc.TM_CCORR_NORMED); if (use_mask && method_accepts_mask) { Imgproc.matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method, mask); } else { Imgproc.matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method); } Core.normalize( result, result, 0, 1, Core.NORM_MINMAX, -1, new Mat() ); double minVal; double maxVal; Point matchLoc; Core.MinMaxLocResult mmr = Core.minMaxLoc( result ); // For all the other methods, the higher the better if( match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF || match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED ) { matchLoc = mmr.minLoc; } else { matchLoc = mmr.maxLoc; } Imgproc.rectangle(img_display, matchLoc, new Point(matchLoc.x + templ.cols(), matchLoc.y + templ.rows()), new Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0); Imgproc.rectangle(result, matchLoc, new Point(matchLoc.x + templ.cols(), matchLoc.y + templ.rows()), new Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0); Image tmpImg = toBufferedImage(img_display); ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(tmpImg); imgDisplay.setIcon(icon); result.convertTo(result, CvType.CV_8UC1, 255.0); tmpImg = toBufferedImage(result); icon = new ImageIcon(tmpImg); resultDisplay.setIcon(icon); } public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) { JSlider source = (JSlider) e.getSource(); if (!source.getValueIsAdjusting()) { match_method = (int)source.getValue(); matchingMethod(); } } public Image toBufferedImage(Mat m) { int type = BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY; if ( m.channels() > 1 ) { type = BufferedImage.TYPE_3BYTE_BGR; } int bufferSize = m.channels()*m.cols()*m.rows(); byte [] b = new byte[bufferSize]; m.get(0,0,b); // get all the pixels BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(m.cols(),m.rows(), type); final byte[] targetPixels = ((DataBufferByte) image.getRaster().getDataBuffer()).getData(); System.arraycopy(b, 0, targetPixels, 0, b.length); return image; } private void createJFrame() { String title = "Source image; Control; Result image"; JFrame frame = new JFrame(title); frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); frame.add(imgDisplay); int min = 0, max = 5; JSlider slider = new JSlider(JSlider.VERTICAL, min, max, match_method); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setPaintLabels(true); // Set the spacing for the minor tick mark slider.setMinorTickSpacing(1); // Customizing the labels Hashtable labelTable = new Hashtable(); labelTable.put( new Integer( 0 ), new JLabel("0 - SQDIFF") ); labelTable.put( new Integer( 1 ), new JLabel("1 - SQDIFF NORMED") ); labelTable.put( new Integer( 2 ), new JLabel("2 - TM CCORR") ); labelTable.put( new Integer( 3 ), new JLabel("3 - TM CCORR NORMED") ); labelTable.put( new Integer( 4 ), new JLabel("4 - TM COEFF") ); labelTable.put( new Integer( 5 ), new JLabel("5 - TM COEFF NORMED : (Method)") ); slider.setLabelTable( labelTable ); slider.addChangeListener(this); frame.add(slider); frame.add(resultDisplay); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } } public class MatchTemplateDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // load the native OpenCV library System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME); // run code new MatchTemplateDemoRun().run(args); } }
Downloadable code : Click here
Code at glance:
import sys import cv2 use_mask = False img = None templ = None mask = None image_window = "Source Image" result_window = "Result window" match_method = 0 max_Trackbar = 5 def main(argv): if (len(sys.argv) < 3): print 'Not enough parameters' print 'Usage:\nmatch_template_demo.py <image_name> <template_name> [<mask_name>]' return -1 global img global templ img = cv2.imread(sys.argv[1], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) templ = cv2.imread(sys.argv[2], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) if (len(sys.argv) > 3): global use_mask use_mask = True global mask mask = cv2.imread( sys.argv[3], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR ) if ((img is None) or (templ is None) or (use_mask and (mask is None))): print 'Can\'t read one of the images' return -1 cv2.namedWindow( image_window, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ) cv2.namedWindow( result_window, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ) trackbar_label = 'Method: \n 0: SQDIFF \n 1: SQDIFF NORMED \n 2: TM CCORR \n 3: TM CCORR NORMED \n 4: TM COEFF \n 5: TM COEFF NORMED' cv2.createTrackbar( trackbar_label, image_window, match_method, max_Trackbar, MatchingMethod ) MatchingMethod(match_method) cv2.waitKey(0) return 0 def MatchingMethod(param): global match_method match_method = param img_display = img.copy() method_accepts_mask = (cv2.TM_SQDIFF == match_method or match_method == cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED) if (use_mask and method_accepts_mask): result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, templ, match_method, None, mask) else: result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, templ, match_method) cv2.normalize( result, result, 0, 1, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, -1 ) minVal, maxVal, minLoc, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result, None) if (match_method == cv2.TM_SQDIFF or match_method == cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED): matchLoc = minLoc else: matchLoc = maxLoc cv2.rectangle(img_display, matchLoc, (matchLoc[0] + templ.shape[0], matchLoc[1] + templ.shape[1]), (0,0,0), 2, 8, 0 ) cv2.rectangle(result, matchLoc, (matchLoc[0] + templ.shape[0], matchLoc[1] + templ.shape[1]), (0,0,0), 2, 8, 0 ) cv2.imshow(image_window, img_display) cv2.imshow(result_window, result) pass if __name__ == "__main__": main(sys.argv[1:])
Explanation
- Declare some global variables, such as the image, template and result matrices, as well as the match method and the window names:
bool use_mask; Mat img; Mat templ; Mat mask; Mat result; const char* image_window = "Source Image"; const char* result_window = "Result window"; int match_method; int max_Trackbar = 5;
Boolean use_mask = false; Mat img = new Mat(), templ = new Mat(); Mat mask = new Mat(); int match_method; JLabel imgDisplay = new JLabel(), resultDisplay = new JLabel();
use_mask = False img = None templ = None mask = None image_window = "Source Image" result_window = "Result window" match_method = 0 max_Trackbar = 5
- Load the source image, template, and optionally, if supported for the matching method, a mask:
img = imread( argv[1], IMREAD_COLOR ); templ = imread( argv[2], IMREAD_COLOR ); if(argc > 3) { use_mask = true; mask = imread( argv[3], IMREAD_COLOR ); } if(img.empty() || templ.empty() || (use_mask && mask.empty())) { cout << "Can't read one of the images" << endl; return -1; }
img = Imgcodecs.imread( args[0], Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR ); templ = Imgcodecs.imread( args[1], Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR );
global img global templ img = cv2.imread(sys.argv[1], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) templ = cv2.imread(sys.argv[2], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) if (len(sys.argv) > 3): global use_mask use_mask = True global mask mask = cv2.imread( sys.argv[3], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR ) if ((img is None) or (templ is None) or (use_mask and (mask is None))): print 'Can\'t read one of the images' return -1
- Create the Trackbar to enter the kind of matching method to be used. When a change is detected the callback function is called.
const char* trackbar_label = "Method: \n 0: SQDIFF \n 1: SQDIFF NORMED \n 2: TM CCORR \n 3: TM CCORR NORMED \n 4: TM COEFF \n 5: TM COEFF NORMED"; createTrackbar( trackbar_label, image_window, &match_method, max_Trackbar, MatchingMethod );
int min = 0, max = 5; JSlider slider = new JSlider(JSlider.VERTICAL, min, max, match_method);
trackbar_label = 'Method: \n 0: SQDIFF \n 1: SQDIFF NORMED \n 2: TM CCORR \n 3: TM CCORR NORMED \n 4: TM COEFF \n 5: TM COEFF NORMED' cv2.createTrackbar( trackbar_label, image_window, match_method, max_Trackbar, MatchingMethod )
- Let’s check out the callback function. First, it makes a copy of the source image:
Mat img_display; img.copyTo( img_display );
Mat img_display = new Mat(); img.copyTo( img_display );
img_display = img.copy()
- Perform the template matching operation. The arguments are naturally the input image I, the template T, the result R and the match_method (given by the Trackbar), and optionally the mask image M.
bool method_accepts_mask = (CV_TM_SQDIFF == match_method || match_method == CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED); if (use_mask && method_accepts_mask) { matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method, mask); } else { matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method); }
Boolean method_accepts_mask = (Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF == match_method || match_method == Imgproc.TM_CCORR_NORMED); if (use_mask && method_accepts_mask) { Imgproc.matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method, mask); } else { Imgproc.matchTemplate( img, templ, result, match_method); }
method_accepts_mask = (cv2.TM_SQDIFF == match_method or match_method == cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED) if (use_mask and method_accepts_mask): result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, templ, match_method, None, mask) else: result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, templ, match_method)
- We normalize the results:
normalize( result, result, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat() );
Core.normalize( result, result, 0, 1, Core.NORM_MINMAX, -1, new Mat() );
cv2.normalize( result, result, 0, 1, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, -1 )
- We localize the minimum and maximum values in the result matrix R by using minMaxLoc().
double minVal; double maxVal; Point minLoc; Point maxLoc; Point matchLoc; minMaxLoc( result, &minVal, &maxVal, &minLoc, &maxLoc, Mat() );
double minVal; double maxVal; Point matchLoc; Core.MinMaxLocResult mmr = Core.minMaxLoc( result );
minVal, maxVal, minLoc, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result, None)
- For the first two methods ( TM_SQDIFF and MT_SQDIFF_NORMED ) the best match are the lowest values. For all the others, higher values represent better matches. So, we save the corresponding value in the matchLoc variable:
if( match_method == TM_SQDIFF || match_method == TM_SQDIFF_NORMED ) { matchLoc = minLoc; } else { matchLoc = maxLoc; }
// For all the other methods, the higher the better if( match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF || match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED ) { matchLoc = mmr.minLoc; } else { matchLoc = mmr.maxLoc; }
if (match_method == cv2.TM_SQDIFF or match_method == cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED): matchLoc = minLoc else: matchLoc = maxLoc
- Display the source image and the result matrix. Draw a rectangle around the highest possible matching area:
rectangle( img_display, matchLoc, Point( matchLoc.x + templ.cols , matchLoc.y + templ.rows ), Scalar::all(0), 2, 8, 0 ); rectangle( result, matchLoc, Point( matchLoc.x + templ.cols , matchLoc.y + templ.rows ), Scalar::all(0), 2, 8, 0 ); imshow( image_window, img_display ); imshow( result_window, result );
Imgproc.rectangle(img_display, matchLoc, new Point(matchLoc.x + templ.cols(), matchLoc.y + templ.rows()), new Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0); Imgproc.rectangle(result, matchLoc, new Point(matchLoc.x + templ.cols(), matchLoc.y + templ.rows()), new Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0); Image tmpImg = toBufferedImage(img_display); ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(tmpImg); imgDisplay.setIcon(icon); result.convertTo(result, CvType.CV_8UC1, 255.0); tmpImg = toBufferedImage(result); icon = new ImageIcon(tmpImg); resultDisplay.setIcon(icon);
cv2.rectangle(img_display, matchLoc, (matchLoc[0] + templ.shape[0], matchLoc[1] + templ.shape[1]), (0,0,0), 2, 8, 0 ) cv2.rectangle(result, matchLoc, (matchLoc[0] + templ.shape[0], matchLoc[1] + templ.shape[1]), (0,0,0), 2, 8, 0 ) cv2.imshow(image_window, img_display) cv2.imshow(result_window, result)
Results
Testing our program with an input image such as:

and a template image:

Generate the following result matrices (first row are the standard methods SQDIFF, CCORR and CCOEFF, second row are the same methods in its normalized version). In the first column, the darkest is the better match, for the other two columns, the brighter a location, the higher the match.



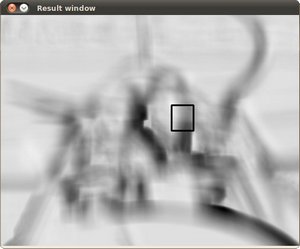


The right match is shown below (black rectangle around the face of the guy at the right). Notice that CCORR and CCDEFF gave erroneous best matches, however their normalized version did it right, this may be due to the fact that we are only considering the “highest match” and not the other possible high matches.
